1. 三大函数:拷贝构造、赋值和析构
标准库太过于复杂,所以写一个基本功能的string
实现如下功能:
int main()
{
String s1();
String s2("hello");
String s3(s1); //copy,构造 *重点
cout << s3 << endl; //重载
s3 = s2; //copy,赋值
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
编译器会给一套构造,string用很不好,如果类带指针,就不能用默认版本,要自己写!
Big Three,三个特殊函数
拷贝构造
拷贝赋值
析构函数:当它死亡时就会被调用
这三个就是big three
ctor和dtor(构造函数和析构函数)
new分配1个字符:new char[1]
如果没有把动态分配的内存及时清理,会内存溢出!
所以需要析构函数!
new和delete之后再讲!
class with pointer members 必须有拷贝构造和拷贝赋值
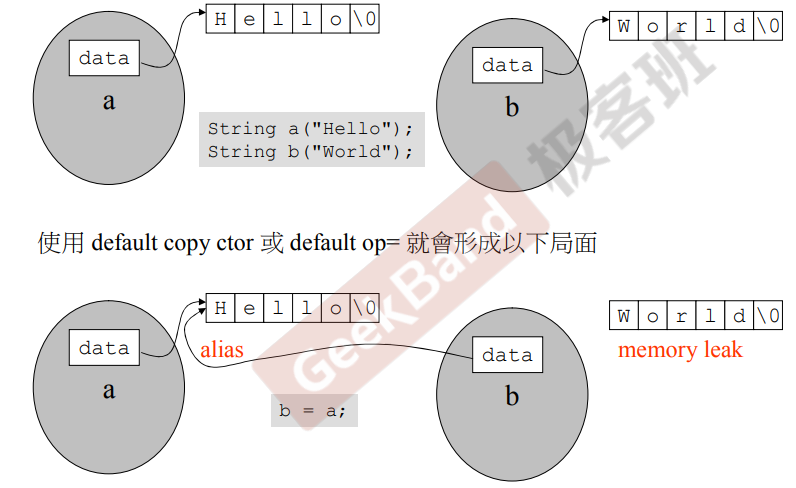
使用默认的浅拷贝,很危险!
拷贝构造函数
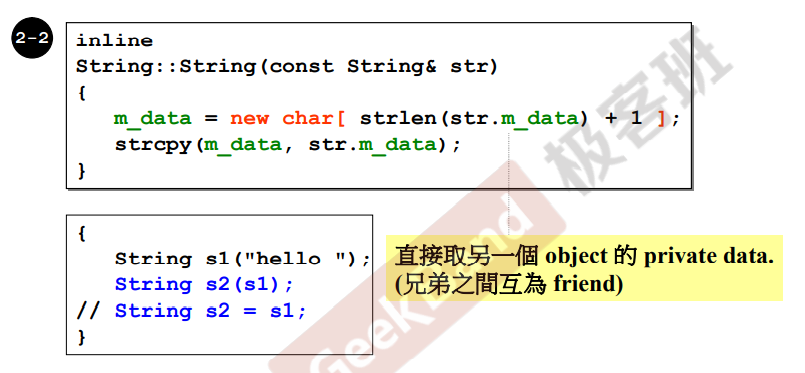
1.创建出一个足够的空间
2.把内容拷贝过去
如果不写这个函数只拷贝指针就是浅拷贝,要避免!
拷贝赋值函数
把左边杀掉,再分配一块右边一样大的空间,再把右边的复制到左边。
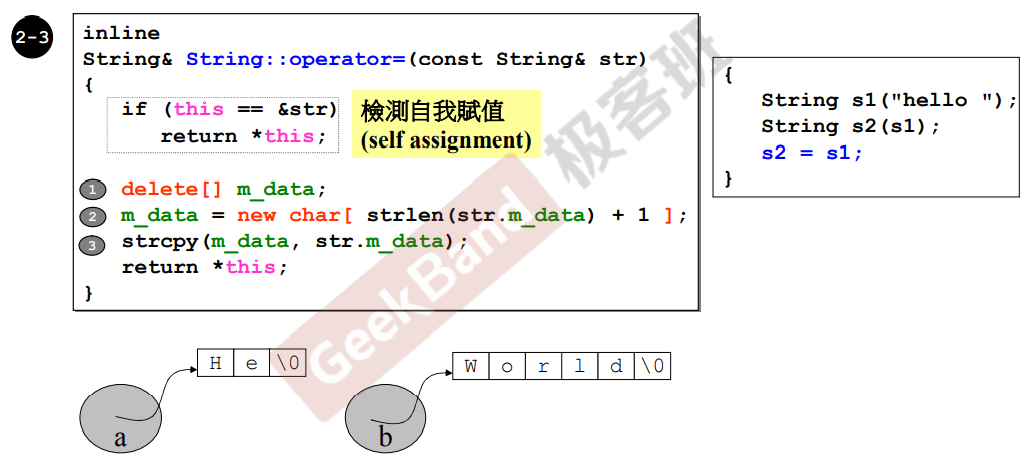
如果不写检测自我赋值,1杀掉以后,a和b都找不到唯一的那个指针了!
所以要写自我赋值检测!
2.堆、栈与内存管理
output函数
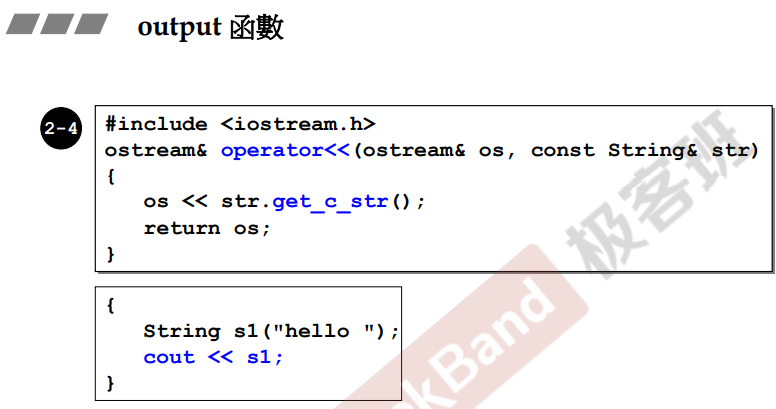
写成全局函数,因为写成成员函数cout会在右边!
所谓栈(stack),所谓堆(heap)
stack,是存在于某作用域的一块内存空间,例如你调用函数,函数本身即会形成一个stack用来放置它所接收的参数,以及返回地址。
在函数本体内声明的任何变量,其所使用的内存块都取自上述stack。
Heap,或system heap是指由操作系统提供的一块global内存空间,程序可动态分配从某个中获得的若干区块(blocks)。
class Complex { … };
...
{
Complex c1(1,2); //栈
Complex* p = new Complex(3); //堆
}上述c1其生命在作用域结束之际就会结束,这种作用域的object,又称为auto object,因为他会被自动清理。
stack local objects 的生命期
class Complex { … };
...
{
stack Complex c1(1,2); //
}上述生命在程序结束后其生命才会结束!
global objects的生命期
class Complex { … };
...
Complex c3(1,2);
int main()
{
}也可以视为stack,其作用域是整个程序!
class Complex { … };
...
{
Complex* p = new Complex;
...
delete p;
}p所指的便是heap object,其生命在被deleted之际结束。
class Complex { … };
...
{
Complex* p = new Complex;
}以上出现内存泄漏,因为当作用域结束,p所指的heap仍然存在,但指针p的生命却结束了,作用域之外再也看不到p,heap就此遗失在内存海里。
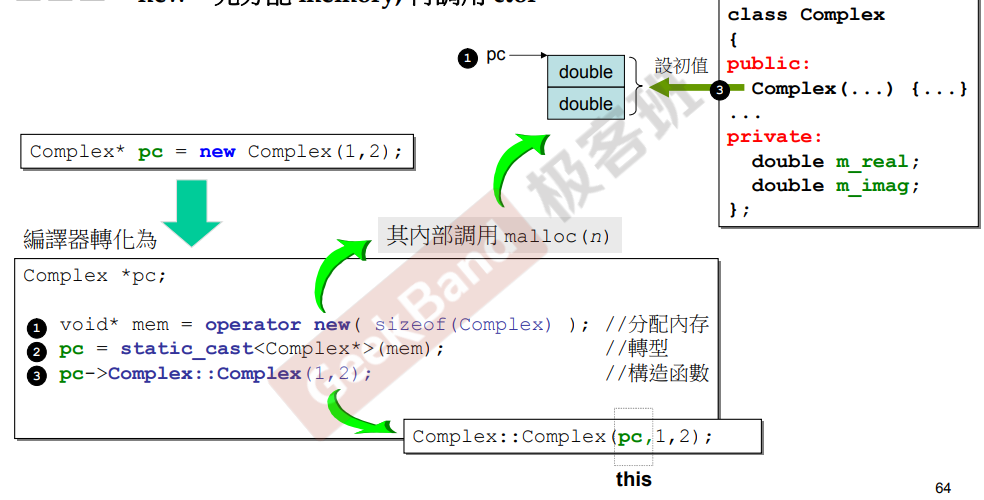
new:先分配memory,再调用ctor
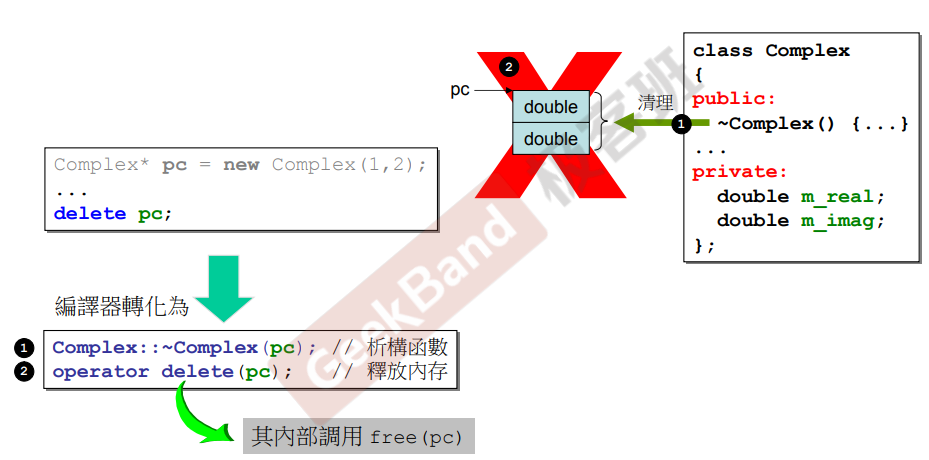
delete:先调用dtor,再释放memory
动态分配所得的内存块 in VC
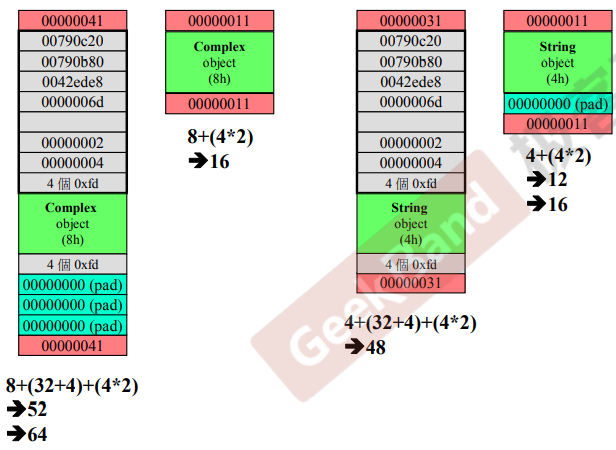
必须是16的倍数,所以从52pad到64
在非调试下,得到的就是16
上下cookie要记录整个的大小!
64的16进制是40,41是因为最后一位是1的话为操作系统给出去的内存,0是操作系统拿到的内存,所以改成41.
16的倍倍数的16位进制最后的4位都是0所以可以借一个来用。
动态分配的array
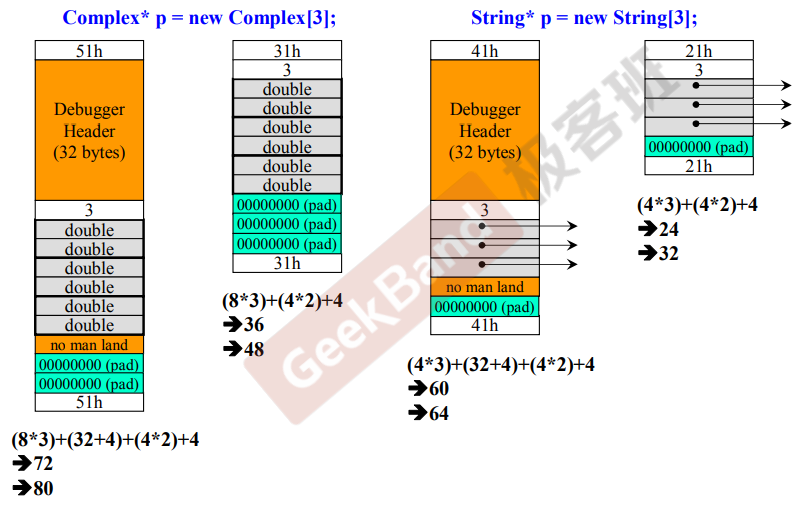
8*3的意思是3个数字,最后+4是因为vc中要在数组的前面声明数组长度!
array new 一定要搭配 array delete
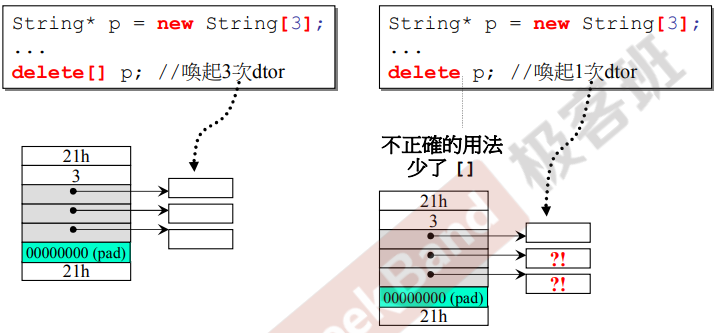
内存泄漏的是只杀掉了第一个指针,剩下的两个都没有杀掉!
指针class复习
string.h
#ifndef __String__
#define __String__
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
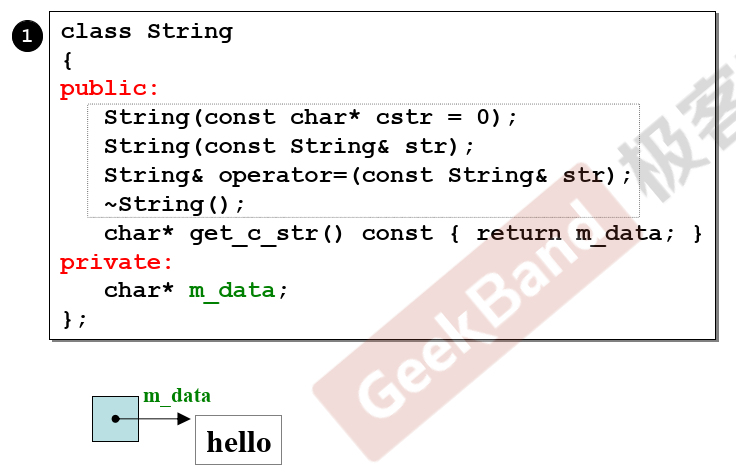
class String {
public:
String(const char* cstr = 0); //拿来当初值
String(const String& str);
String& operator=(const String& str);
~String();
char* get_c_str() const { return m_data; }
private:
char* m_data;
};
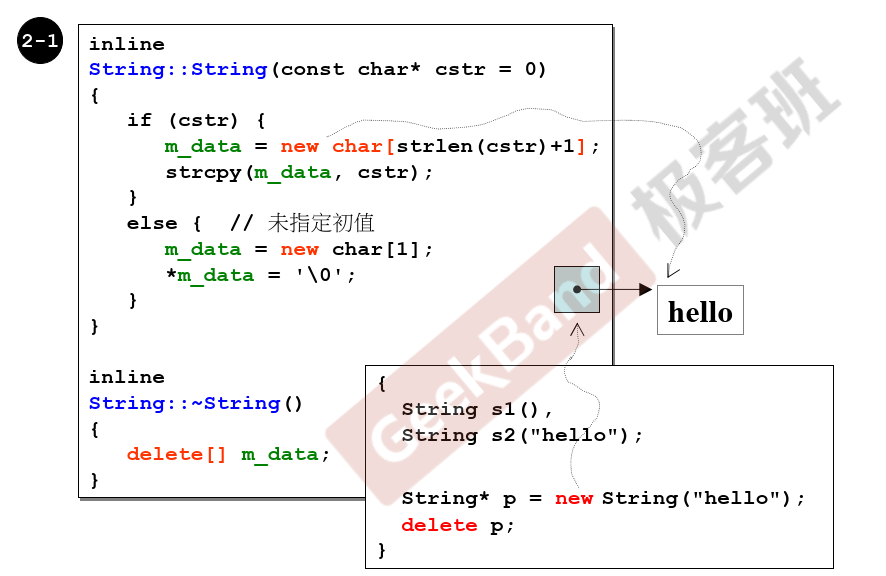
inline String::String(const char* cstr)
{
if (cstr) {
m_data = new char[std::strlen(cstr) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, cstr);
}
else {
m_data = new char[1];
*m_data = '\0';
}
}
inline
String::~String()
{
delete[] m_data;//array new
}
inline
String::String(const String& str)
{
m_data= new char[std::strlen(str.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
}
inline
String& String::operator=(const String& str)//&引用
{
if (&str == this) {//&取地址
return *this;
}
delete[] m_data;
m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
return *this;
}
std::ostream& //back add ostream
operator << (std::ostream& os, const String& str) //cout will change
{
os << str.get_c_str();
return os;
}
#endifstring_test.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
String s1("hello");
String s2("world");
String s3(s2);
cout << s3 << endl;
s3 = s1;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
- 本文链接:https://www.tjzzz.com/posts/f6964998.html
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均默认采用 许可协议。


