本文是学习肖勇大神的点云课程总结的笔记,仅供个人学习使用。
肖勇
Mapping & Localization Technical Specialist @ Lucid Motors,主要从事无人车地 图和定位算法研发。先后参与 Lyft、百度无人车 项目开发。密歇根大学土木工程博士,中科院遥 感与数字地球研究所地图学硕士,武汉大学测绘 工程学士。
点云数据及获取
- 定义
- 点云:三维点的数据集合
- 属性
- 三维坐标
- 强度
- 颜色
- 时间戳
分类
点云组织形式:
- organized: the point cloud is laid out as a 2D array of points that resembles an image like structure -
- unorganized: the point cloud is a list of points.
- 点云获取方式
- 激光扫描仪
- 星载
- 机载
- 地面
- 移动
- 深度相机(depth Camera)
- 双目相机(stereo Camera)
- 光学相机多视角重建
- 激光扫描仪

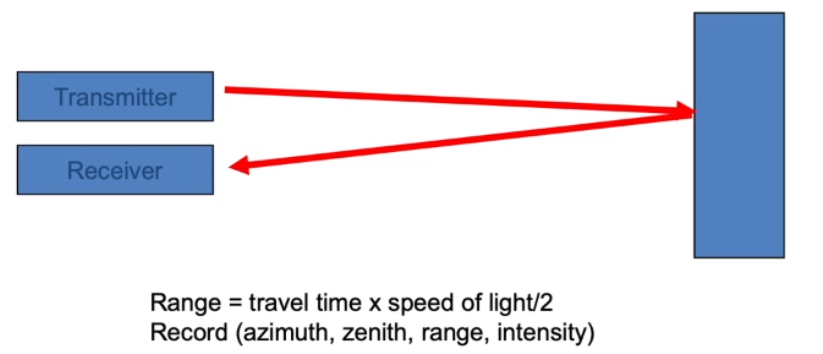
激光扫描仪
工作原理:time of flight
分类
- 星载:卫星
- 机载:飞机,无人机
- 地面:三脚架上固定
- 移动:车辆,机器人等
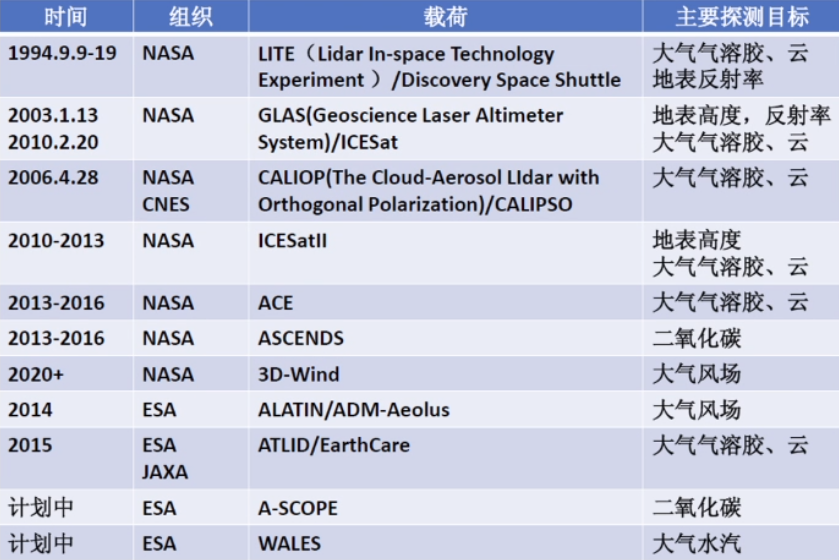
星载激光雷达
- 常见系统
- GLAS星载激光雷达 系统(Geoscience Laser Altimeter System)
- CALIOP星载激光雷 达
- ALADIN星载多普勒 激光雷达
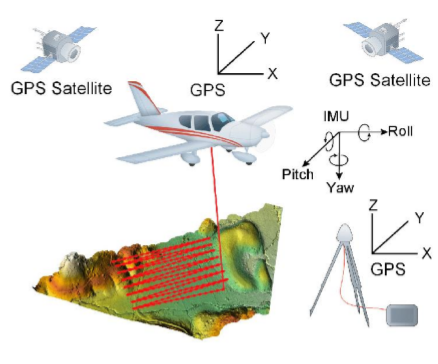
机载激光雷达
- 机载激光雷达
- 使用配有 GPS/IMU的飞机(无人机) 获取大范围的点云
- 特点
- 精度高:10cm
- 大尺度测绘
- 应用领域
- 大尺度(城市级别)测绘
- DEM
- 正射影像 (高精度相机)
地面激光雷达
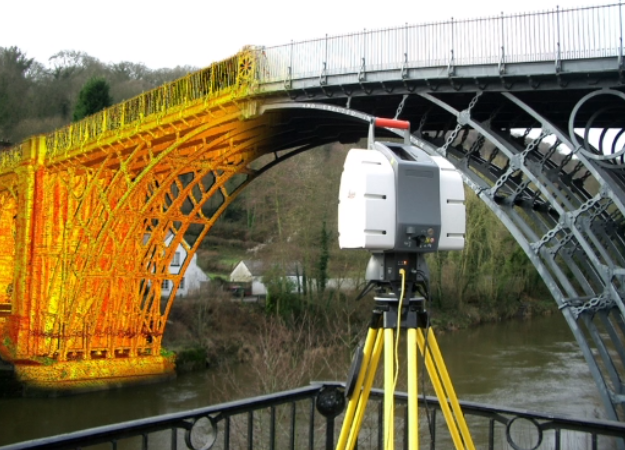
- 地面激光雷达
- 激光雷达通常固定在三角架上,进行 较大范围扫描获取点云。
- 特点
- 精度高: 可达到 mm
- 距离远:可达到400m
- 扫描速度快: Leica RTC360 1s 采集 ~200万点云
- 应用
- 文物三维扫描建模
- 地形测量

移动激光雷达
移动激光雷达
- 激光雷达通常跟着移动物体( 机器人无人车),进行较大范 围扫描获取点云
特点
- 精度高: cm
- 距离远:~240m
- 扫描速度快: 10Hz, 200万点 云每秒
应用
无人车,机器人
街景测量

Point Cloud created by Velodyne Lidar’s Alpha Prime sensor
深度相机
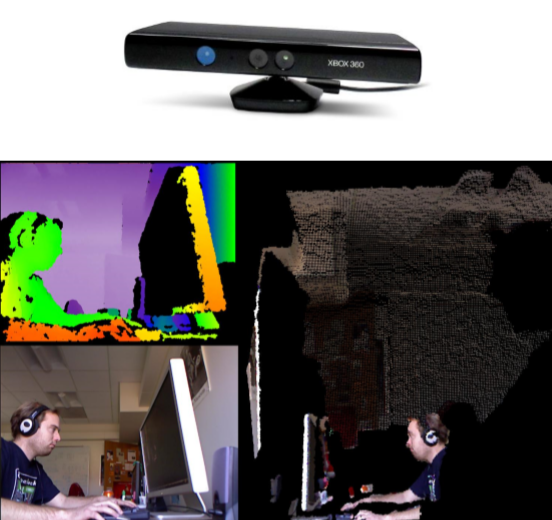
- 深度相机
- 通过近红外激光器把具有结构特征 的光线投影到物体上,通过红外摄 像头采集得到深度信息。
- 特点
- 成本低,计算量小
- 主动光源,夜晚也可用
- 观测该范围和距离有限
- 应用
- 室内机器人
- AR/VR

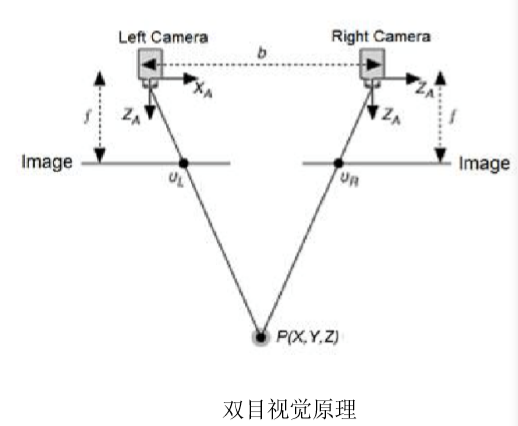
双目相机
- 使用两个相机从不同位置获取物体的 两幅图像,通过计算对应点的位置偏 差,使用三角原理(Triangulation) 计算点的三维坐标
- 特点
- 成本低
- 室内室外都适用
- 对环境光敏感
- 基线限制了测量范围
光学相机多视角重建
SFM 运动结构恢复(Structure from motion)
- 给出多幅图像及其图像特征点的对应集合 ,估计3D点的位置和摄像机姿态(运动)
特点
成本低
使用高精度相机和更稳定的平台(有 GPS/IMU)可以进行高精度测量
计算量大
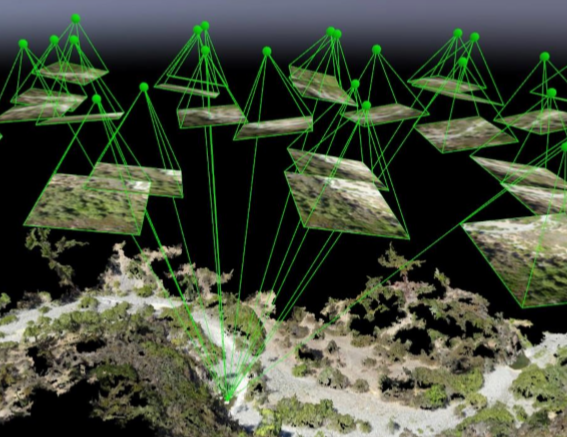
Credit to http://gsp.humboldt.edu/OLM/Courses/GSP_216_Online/lesson8-2/SfM.html
点云数据处理
点云滤波(filtering)
- 检测和移除点云中的噪声或不感兴趣的点
- 分类
- 基于统计信息 (statiscal-based)
- 基于领域 (neighbor-based) 基于投影(projection-based)
- 基于信号处理(singal processing based)
- 基于偏微分方程(PDEs-based)
- 其他方法:voxel grid fitlering, quadtreebased, etc.
- 常用方法
- 基于体素(voxel grid)
- 移动平均最小二乘(Moving Least Squares)

点云匹配 (point cloud registration)
- 估计两帧或者多帧点云之间的 rigid body transformation 信息,将所有帧的点云配准在同 一个坐标系。
- 分类
- 初/粗匹配: 适用于初始位姿差别大的两帧点云
- 精匹配:优化两帧点云之间的变换
- 全局匹配:通常指优化序列点云匹配的误差, 如激光 SLAM,两帧之间匹配,全局匹配
- 常用方法
- 基于 Iterative Closest Point (ICP)的方法
- 基于特征的匹配方法
- 深度学习匹配方法
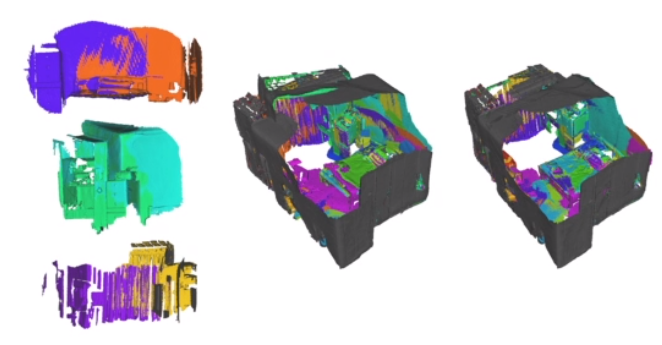
Credit to http://geometryhub.net/en/notes/registration
- Iterative Closest Point (ICP)Registration
- Given two scans 𝑃 and 𝑄, initial transformation between them 𝑅,𝑡
- Iterate
- Find some pairs of closest points (𝑝𝑖,𝑞𝑖)
- Optimize 𝑅,𝑡 to minimize
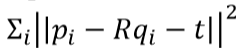
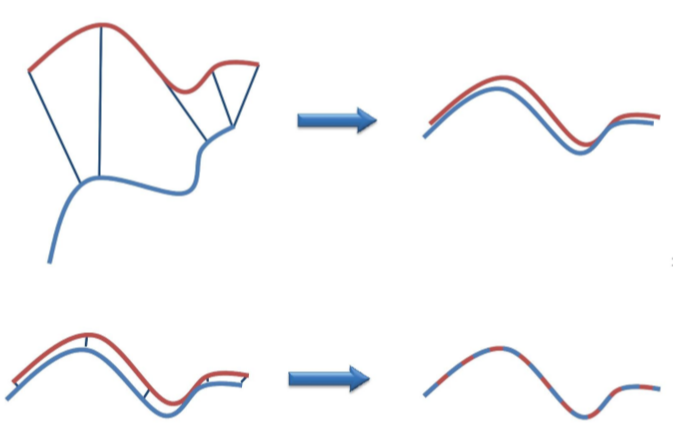
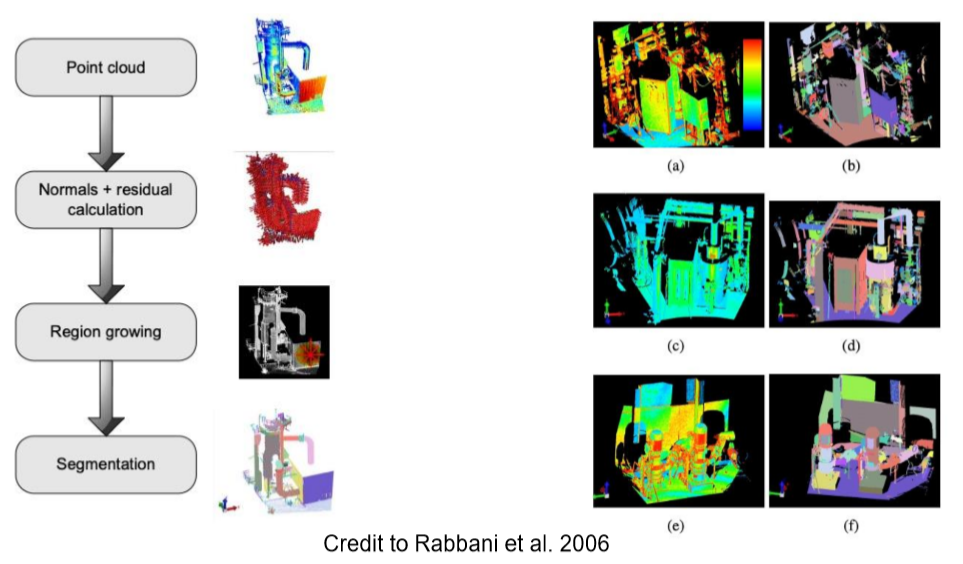
点云分割 (segmentation)
- 根据空间、集合等特征将点划分为不同的集合。
- 常用方法
- 基于边缘的方法:变成图像,使用边缘信息
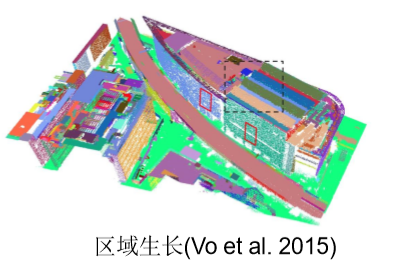
- 基于区域生长
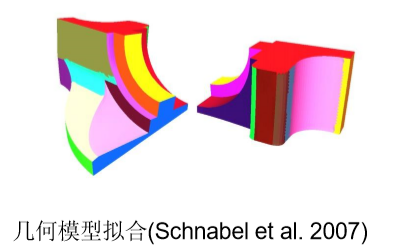
- 几何模型拟合:拟合平面,球形,圆柱等
- Segmentation using smoothness constraint
点云目标检测 (object detection)
从点云中检测某类物体
方法:
- 传统机器学习方法
- 深度学习方法
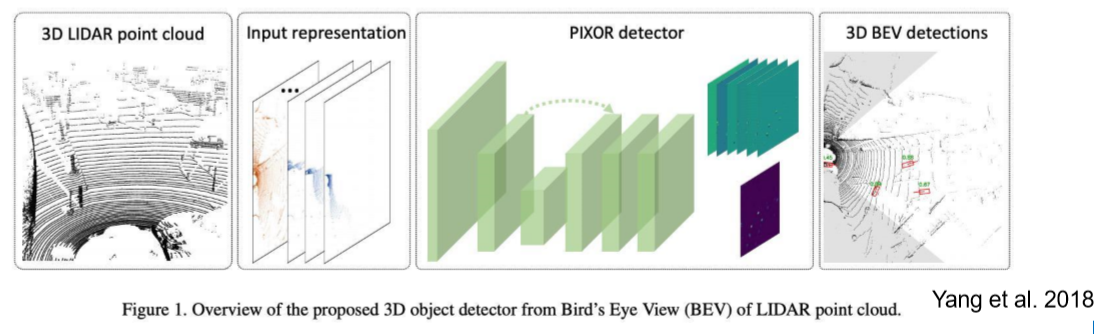
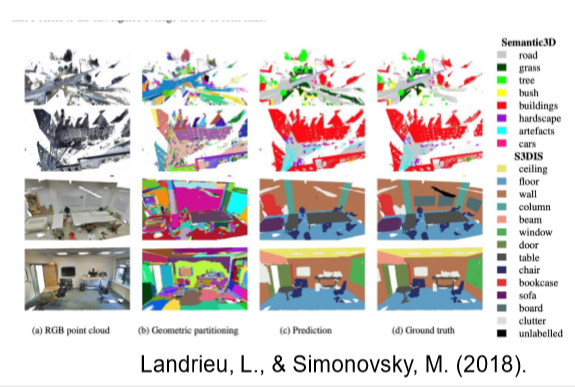
点云分类 (classification)/语义分割(Semantic Segmentation)
为每个点云分配一个语义标签
方法:
- 传统机器学习
- 深度学习
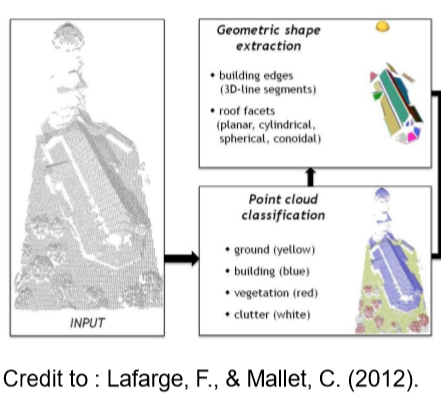
模型重建 (model reconstruction
从点云中获取更精简更紧凑的模型,如获取 mesh 模型。
常见的 3D shape representation: 深度图,点云 ,体素,网格(mesh)
常用方法:
- Delaunay Mesh Generation
- Finite Element Mesh Generation.
- Marching cube
常用软件及开源
CloudCompare
开源,且支持多平台(Windows, Mac, Linux)
- 支持常见的点云数据格式,简单的 点云编辑
- 支持用户自己添加插件和增加新功 能 (如 Ransac, Poisson Mesh Reconstruction, Classification with CANUPO)
- 适合于点云可视化,简单编辑或者处理
Meshlab
- 处理和编辑3D三角形网格的开源系 统
- 主要是编辑,清理,修复,检查, 渲染,纹理和转换网格的工具
- 3D Acquisition: color mapping and texturing Cleaning 3D models
- 支持多平台(Win,Linux, Mac)
部分商业软件
- Microstation TerraSolid (Bentley):航测,主要适用于机载雷达,获取 DEM 和建筑建模等
- Global Mapper Lidar Moduel:主要处理机载激光雷达数据,分类,建模,生成 DEM等
- LiDAR 360 (数字绿土):林业资源调查,地形测绘等
- 点云魔方(中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所):植被应用,电力巡线等
- ENVI LiDAR; ArcGIS:含有部分点云处理模块,主要用于遥感和林业
- Cyclone, Cloudworx, TruView: Leica徕卡开发,主要用于其地面激光雷达和移动(背包式)激光
雷达数据处理 - Riscan Pro:主要用于处理 Riegl 瑞格地面激光雷达数据
- RealWorks(Trimble)
- Polyworks (Innovmetric); Geomagic (3D systems):逆向工程,主要用于机械测量
开源库
- PCL (Point cloud library)
- Filter
- Segmentation
- Registration
- Keypoints
- Recognition
- 特点
- 支持多平台(Win,Linux, Mac)
- 功能齐全,可扩展性好
- 广泛用于机器人,很多开源算法和 系统(ROS)
- Open3D
- Surface alignment
- 3D machine learning support with PyTorch and TensorFlow
- GPU acceleration for core 3D operation
- 特点 •
- 支持多平台
- python集成成熟,可和 Pytorch, Tensorflow 集成
参考文献
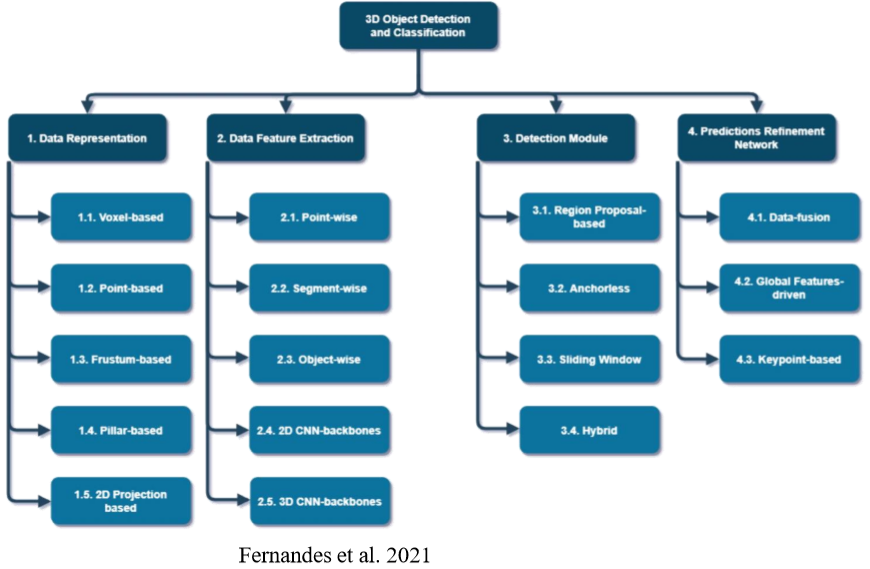
- Fernandes, D., Silva, A., Névoa, R., Simões, C., Gonzalez, D., Guevara, M., Novais, P., Monteiro, J. and Melo-Pinto, P., 2021. Pointcloud based 3D object detection and classification methods for self-driving applications: A survey and taxonomy. Information Fusion,68, pp.161-191.
- Florent Lafarge, Clément Mallet. Creating large-scale city models from 3D-point clouds: a robust approach with hybrid representation. International Journal of Computer Vision, Springer Verlag, 2012, 99 (1), pp.69-85. ffhal-00759265f
- Han, X.F., Jin, J.S., Wang, M.J., Jiang, W., Gao, L. and Xiao, L., 2017. A review of algorithms for filtering the 3D point cloud. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 57, pp.103-112.
- Landrieu, L., & Simonovsky, M. (2018). Large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation with superpoint graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 4558-4567).
- Lin, X. and Zhang, J., 2014. Segmentation-based filtering of airborne LiDAR point clouds by progressive densification of terrain segments. Remote Sensing,6(2), pp.1294-1326.
- Rabbani, T., Van Den Heuvel, F. and Vosselmann, G., 2006. Segmentation of point clouds using smoothness constraint. International archives of photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information sciences,36(5), pp.248-253.
- Schnabel, R., Wahl, R., & Klein, R. (2007, June). Efficient RANSAC for point‐cloud shape detection. In Computer graphics forum
- Seif, H.G. and Hu, X., 2016. Autonomous driving in the iCity—HD maps as a key challenge of the automotive industry. Engineering, 2(2), pp.159-162
- Vo, A. V., Truong-Hong, L., Laefer, D. F., & Bertolotto, M. (2015). Octree-based region growing for point cloud segmentation. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,104, 88-100.
- Yang, B., Luo, W. and Urtasun, R., 2018. Pixor: Real-time 3d object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 7652-7660).
- Wang, N., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Fu, Y., Liu, W. and Jiang, Y.G., 2018. Pixel2mesh: Generating 3d mesh models from single rgb images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (pp. 52-67).

I'm so cool. Please give me money.
- 本文链接:https://www.tjzzz.com/posts/98b3189b.html
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均默认采用 许可协议。